South Korea’s population is changing rapidly—and understanding how the country’s age structure and regional demographics are shifting in 2025 can offer insight into its future. Whether you’re interested in moving to Korea, doing business here, or just curious about societal trends, this post breaks down the key aspects of South Korea’s population in 2025 in an easy-to-understand way.
What Is the Total Population of Korea in 2025?
As of 2025, South Korea’s total population is estimated to be slightly over 51 million. But it’s not just the number of people that matters—it’s how that population is distributed by age and across cities.
One of the most pressing demographic issues in Korea today is population aging. While the overall population is declining slightly due to low birth rates, the number of elderly people is rising fast. This shift is already influencing everything from healthcare services to school enrollments and job market trends.
Age Distribution: Korea Is Now a Super-Aged Society
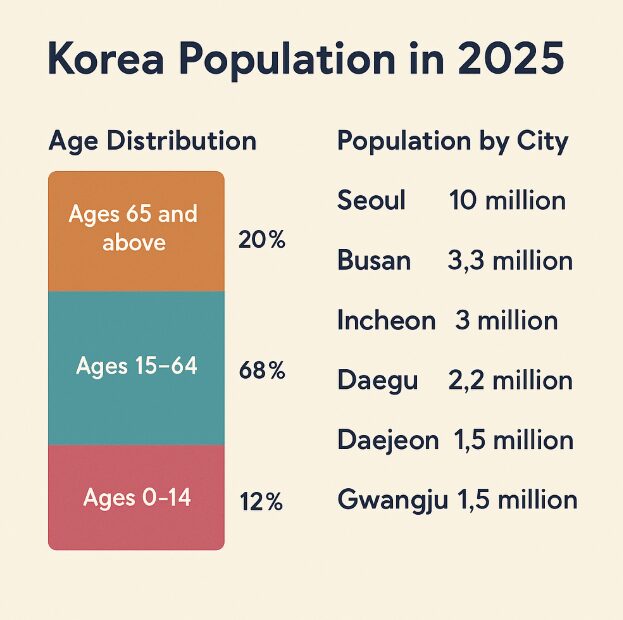
In 2025, South Korea is officially classified as a “super-aged” society, meaning more than 20% of the population is aged 65 or older. That percentage is expected to increase even more over the next decade.
Here’s a general breakdown of the age distribution:
Ages 0–14: about 12%
Ages 15–64: approximately 68%
Ages 65 and above: over 20%
This means fewer children are being born, the working-age population is shrinking, and more resources are being directed toward elder care. For example, schools in some rural areas are closing due to lack of students, while cities are expanding medical facilities to support the growing number of elderly citizens.
Regional Population Differences: Not All Cities Are Equal
When looking at Korea’s population by city, it becomes clear that people are concentrated in a few major urban areas.
Seoul
Still the largest city in the country, Seoul has close to 10 million residents in 2025. However, its population has been slowly decreasing as housing prices and urban density push people outward.
Gyeonggi Province
This area surrounding Seoul continues to grow. Affordable housing and access to transportation make Gyeonggi one of the most popular residential regions. Cities like Suwon, Seongnam, and Yongin are seeing steady population increases.
Busan
The second largest city, Busan, has a population of around 3.3 million. While still vibrant and coastal, it’s facing similar aging challenges as the rest of the country.
Incheon
Home to Korea’s largest airport and a growing tech industry, Incheon has around 3 million residents and continues to attract younger workers.
Sejong
Sejong is one of the fastest-growing cities, thanks to government decentralization efforts. It has a younger population on average compared to Seoul or Busan.
Rural Regions
In contrast, many rural towns and provinces are facing steep population decline. With fewer births and young people moving to cities, some areas are being left with primarily elderly residents and very limited local infrastructure.
How These Trends Are Changing Korean Society
The shifting population is already influencing every part of Korean life.
Education: With fewer children, some schools are merging or closing. University admissions may become less competitive, but there will also be fewer students overall.
Employment: As the working-age population shrinks, some industries are experiencing labor shortages. There is growing interest in automation, AI, and robotics to fill the gaps.
Healthcare: More resources are going into elder care, chronic disease management, and long-term care centers.
Housing: The real estate market is being reshaped. Some areas are seeing oversupply due to migration away from smaller towns, while areas around Seoul continue to experience high demand.
Social Services: Welfare and pension systems are under pressure as the ratio of workers to retirees becomes imbalanced.
What Foreigners Should Know About Korea’s Demographic Shift
If you’re considering working, studying, or living in Korea, these population trends may directly or indirectly affect you.
For example:
There may be more career opportunities in healthcare, elderly services, and tech-related industries due to shifting demand.
Government policies are increasingly foreigner-friendly, especially in regions that need labor or want to grow international communities.
Certain cities and provinces may offer housing subsidies or visa incentives to attract foreign residents.
If you’re planning to raise a family in Korea, you’ll find excellent healthcare and education infrastructure—but possibly fewer children for yours to grow up around, especially outside of big cities.
It’s also worth noting that Korean society is slowly becoming more multicultural. As the native population declines, the role of international workers, students, and long-term residents is becoming more central to sustaining the economy and culture.
Korea’s Population in 2025: What to Expect Moving Forward
Korea’s population story in 2025 is one of imbalance, transition, and opportunity. The population is aging, but not everywhere and not equally. Some regions are bustling and youthful, while others are shrinking and aging rapidly.
This creates opportunities for innovation in healthcare, urban planning, housing, education, and even immigration. Korea is beginning to explore new strategies—from encouraging childbirth to inviting more foreigners—to adapt to these realities.
As we look ahead, demographic change will continue to be one of the biggest forces shaping the country. If you’re living in Korea or planning to visit long-term, understanding these population trends can help you make smarter decisions about where to live, work, and build a future.